Aim:
Improves the signal-to-noise ratio of images without degrading seriously edge contrast and resolution.
Method:
Anisotropic diffusion is now a well-established technique (see Perona & Malik, 1990), based on the resolution of partial differential equations which make the diffusion faster within objects or regions, and slower across edges.
User interface:
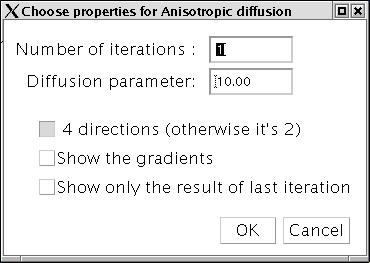
Number of iterations: chosen by the user
Diffusion parameter: depends on the amount of noise in the image.
Directions: 4 ==> 8-connexity (default value) 2 ==> 4-connexity
Shows the gradients: unclicked: No (default value); clicked: yes
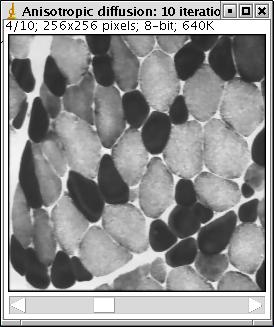
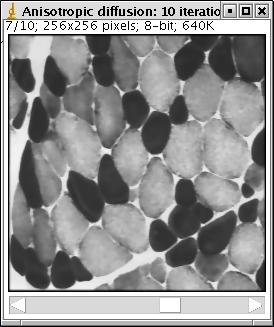
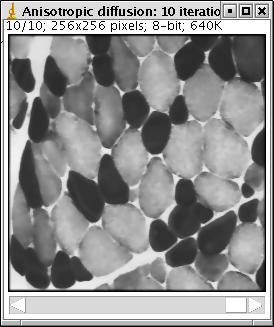
Show only the result of last iteration : unclicked (default value): yes; clicked: a stack of images is produced, one for each iteration (see the illustration below)
Illustration:
Improves the signal-to-noise ratio of images without degrading seriously edge contrast and resolution.
Method:
Anisotropic diffusion is now a well-established technique (see Perona & Malik, 1990), based on the resolution of partial differential equations which make the diffusion faster within objects or regions, and slower across edges.
User interface:

Number of iterations: chosen by the user
Diffusion parameter: depends on the amount of noise in the image.
Directions: 4 ==> 8-connexity (default value) 2 ==> 4-connexity
Shows the gradients: unclicked: No (default value); clicked: yes
Show only the result of last iteration : unclicked (default value): yes; clicked: a stack of images is produced, one for each iteration (see the illustration below)
Illustration: